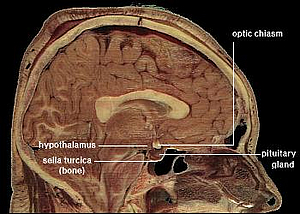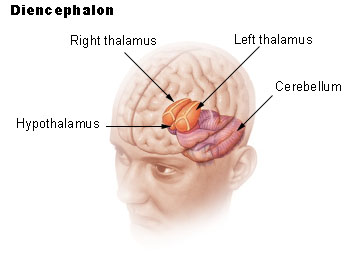
Location of the Centre of Peace (Shanti Kendra)
Controls Emotions
The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The hypothalamus, (from Greek ὑποθαλαμος = under the thalamus) is located below the thalamus, just above the brain stem. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is roughly the size of an almond.
The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the Autonomic Nervous System. It synthesizes and secretes neurohormones, often called hypothalamic-releasing hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and circadian cycles.
It plays important role in emotions of pain and pleasure.