
The thymus gland is situated in the chest between the two lungs, rests on the upper portion of the heart and extends up into the neck. (See fig. III). This gland is believed to control the physical growth of children up to the 14th year of age. During this time it holds other glands particularly the sex gland in check and delays puberty and furthers normal brain development.
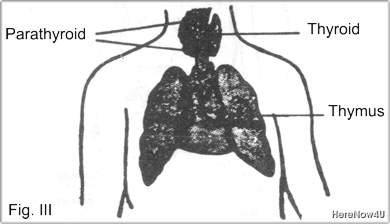
The thymus is a lymphoid organ since it contains closely packed lymphocytes. Besides the function mentioned above, the thymus exerts an influence on the lymphonodes, spleen and other lymphatic tissues so that they too gain the ability to produce lymphocytes and foster the development of immuno-competent cells (T-Cells) by means of a hormone.
 Acharya Mahaprajna
Acharya Mahaprajna

